
Micosis/Hongos
Black or brown spot on pear trees: what it is, how it occurs, and how to remove it effectively.
Black Or Brown Pear Tree Spot
Stemphylium Vesicarium
Pathogen:
Fungus
Type:
Risk to the plant:
HIGH


DESCRIPTION
WHO CAUSES IT?
Stemphylium vesicarium is a phytopathogenic fungus that causes serious diseases in various plants, especially pear trees. This fungus develops through a series of complex stages. It begins with the production of spores, which are released into the environment and can be dispersed by wind or rain. When the spores find a favorable environment, they germinate and form a mycelium that penetrates the plant tissues. The mycelium grows and branches, absorbing nutrients and producing toxins that damage plant tissues. Under suitable conditions, the fungus produces new sporangia, completing its development cycle and allowing the release of more spores to initiate new infections. This cycle can repeat several times during the growing season, increasing the spread of the disease.
SYMPTOMS
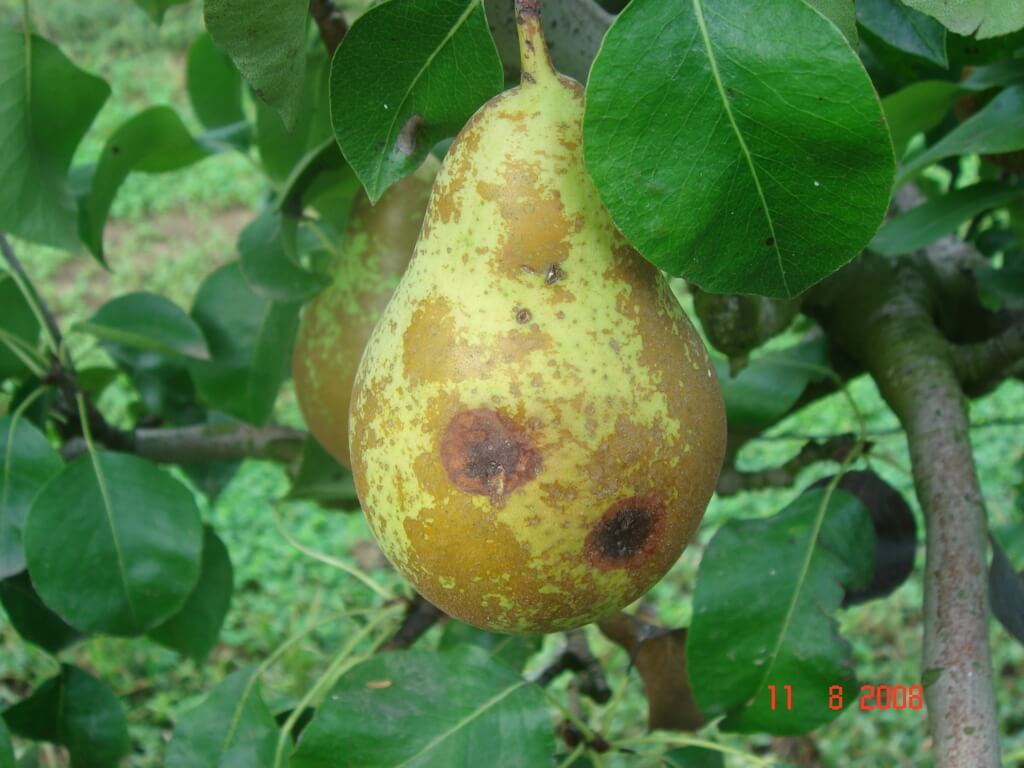
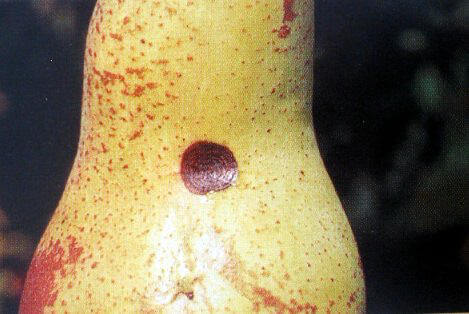
The disease caused by Stemphylium vesicarium on pear trees is known as pear black or brown spot. This disease is characterized by the appearance of dark Taches on the leaves, fruits and branches of the pear tree, which can lead to a significant reduction in the quality and quantity of the harvest. Infected leaves develop small Taches that progressively enlarge and turn dark brown or black. On fruits, lesions can be sunken and surrounded by a yellowish halo, affecting their appearance and commercial value. The branches may also have lesions, which weaken the plant and make it more susceptible to other diseases.
- Appearance of dark Taches on the leaves.
- Sunken lesions on the fruits with yellowish halos.
- Taches on the branches that weaken the plant.
- Loss of quality and quantity of the harvest.
- Premature defoliation.
- Deformation of the fruits.


TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY
20°C - 30°C
70% - 90%

HOW IS IT SPREAD?
Wind, Rain, Contact with contaminated tools, Infected plant material

HOW TO REMOVE IT?
Home remedies
There are no home treatments
Chemical treatments
• BOSCALIDE 25.2% + PYRACLOSTROBIN 12.8% [WG] P/P
• CAPTAIN 80% [WG] P/P
• CIPRODINIL 30% [EC] P/V
• CIPRODINIL 37.5% + FLUDIOXONIL 25% [WG] P/P
• DIFENOCONAZOLE 25% [EC] P/V
• FLUDIOXONIL 50% [WG] P/P
• FLUOPYRAM 20% + TEBUCONAZOLE 20% [SC] P/V
• FLUXAPYROXAD 30% [SC] P/V
• POTASSIUM PHOSPHONATES 66% + CAPTAN 36% [SC] P/V
• KRESOXIM-METHYL 25% + DIPHENOCONAZOLE 12.5% [WG] P/P
• KRESOXIM-METHYL 50% [WG] P/P
• MEFENTRIFLUCONAZOLE 7.5% [SC] P/V
• PIRACLOSTROBIN 20% [WG] P/P
• TEBUCONAZOLE 20% [EW] P/V
• TEBUCONAZOLE 25% [EC] P/V
• TEBUCONAZOLE 25% [EW] P/V
• TEBUCONAZOLE 25% [WG] P/P
• TRIFLOXISTROBIN 50% [WG] P/P
Authorized treatments in organic farming
-
Insect allies
PREDATORY MITES
LADYBUGS
LACEWINGS
PARASITIC WASPS
HOVERFLIES OR PARASITIC FLIES
PREDATORY BUGS
There are no natural allies
Mycodiplosis oidii (predatory mosquito)
EFFECTIVE PRODUCTS TO ELIMINATE THIS DISEASE
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Effective against all types of fungi
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
- Select pear varieties resistant to Stemphylium vesicarium.
- Implement crop rotation to avoid the accumulation of inoculum in the soil.
- Maintain good air circulation inside the garden to reduce humidity.
- Carry out appropriate pruning to eliminate infected branches and improve ventilation.
- Apply preventive fungicides at critical moments, following technical recommendations.
- Regularly monitor the garden to detect and eliminate affected plants.
- Avoid sprinkler irrigation to reduce the spread of spores.
- Use traps or physical barriers to prevent the spread of the fungus.
- Carry out adequate cleaning of the tools and equipment used in the garden.
























