Alternariosis
WHAT IT IS AND HOW TO ELIMINATE
Plantas decorativas de jardín y/o interior
Alternariosis
Alternaria Sp.
Pathogen:
Fungus
Type:
Risk to the plant:
HIGH
Alternariosis

WHO CAUSES IT?
Alternaria sp. It is a genus of filamentous fungi that includes several plant pathogenic species. These fungi reproduce using asexual spores known as conidia, which are dispersed by wind, water, and direct contact. Alternaria can survive on infected plant debris and in soil for long periods. Under favorable conditions, spores germinate and penetrate plant tissues through wounds or stomata. The fungus produces toxins that kill plant cells, allowing the pathogen to feed on dead tissues. Alternaria is especially active in conditions of high humidity and moderate to warm temperatures, which facilitates its spread and the initiation of new infections. This pathogen has the ability to form spores rapidly, allowing it to multiply and cause epidemics in a short period of time.
SYMPTOMS
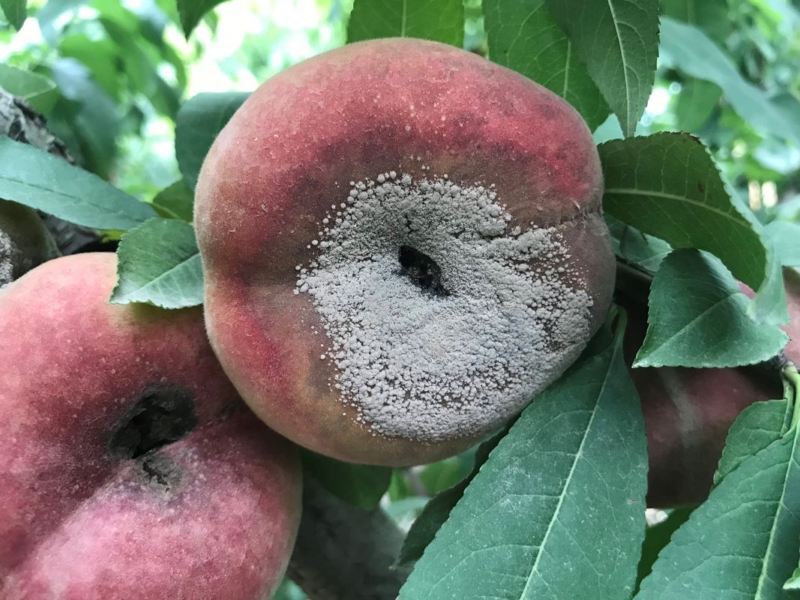
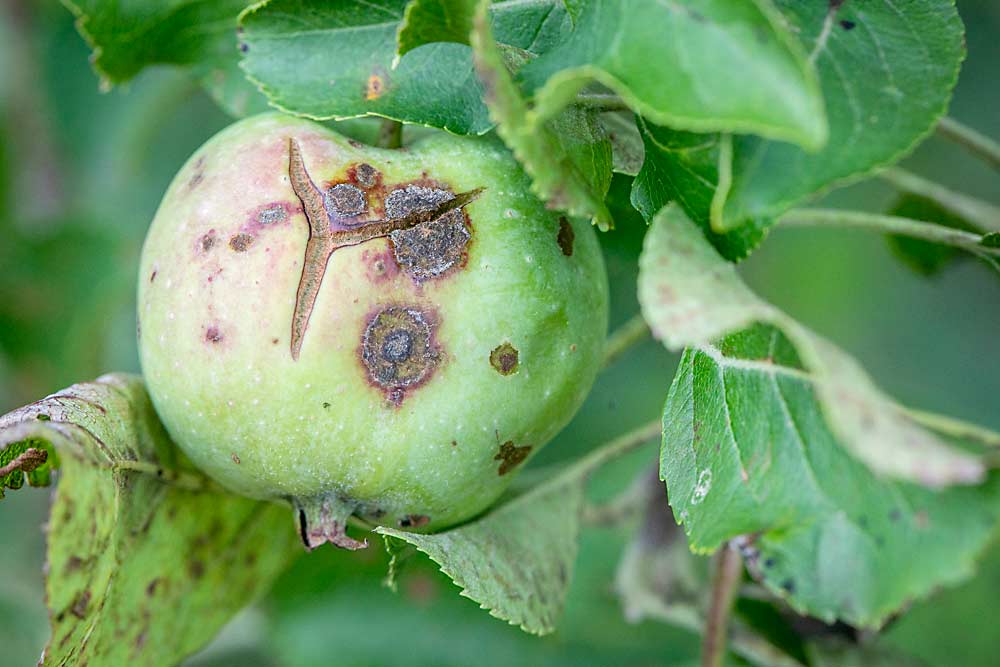
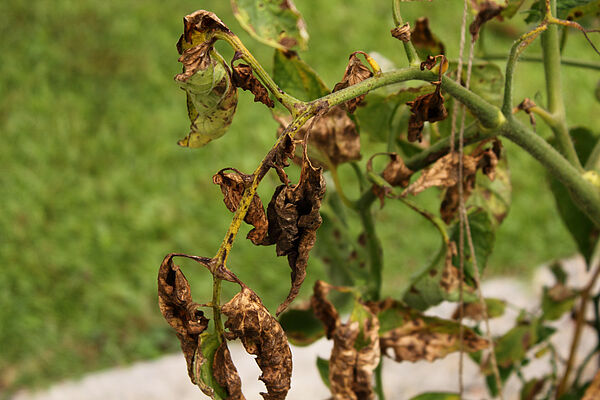
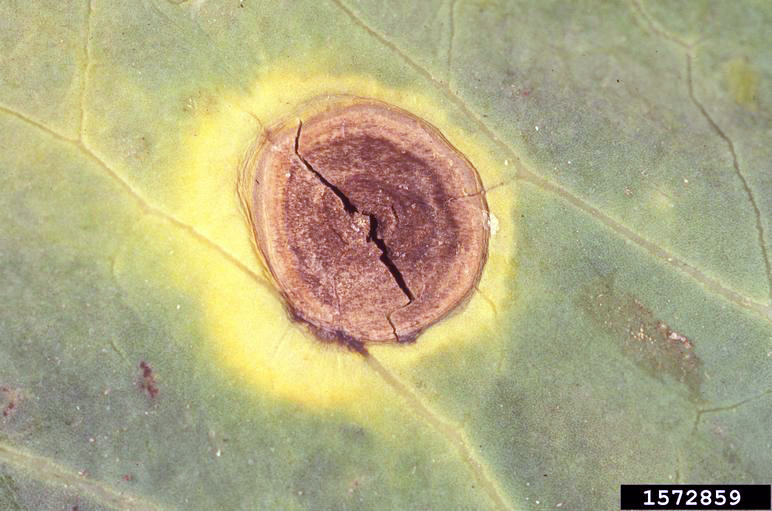
Alternariosis is a disease that affects various plants, manifesting mainly in the leaves, stems and fruits.
- Appearance of brown or black Taches on the leaves, often with yellow edges.
- Necrotic lesions that can expand and join together, causing large areas of dead tissue.
- Dark, sunken Taches on the stems and fruits, which can lead to rot.
- Premature defoliation, especially in high humidity conditions.
- Reduction in the photosynthetic capacity of the plant, weakening it and reducing its performance.
- Appearance of dark mold in affected areas.
- Decomposition and premature fruit fall.
- Discoloration and wilting in advanced stages of infection.


DEVELOPMENT CONDITIONS
Temperature:
18°C - 25°C
Humidity:
80% - 90%
HOW IS IT SPREAD?
Wind, water, contaminated garden tools, direct contact with infected plants, insect vectors, infected seeds
HOW TO ELIMINATE IT?
Home treatments
Natural allies
There are no natural allies
Chemical treatments
RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS TO ELIMINATE THE PEST
REPELLENT PLANTS
-
RECOMMENDATIONS
- Remove leaves and remains of diseased plants from the ground.
- Avoid wetting the leaves when watering, always do it at the base.
- Improves ventilation between plants to reduce humidity.
- Use resistant varieties if available.
- Apply organic products such as copper or horsetail extract.
- Do not always plant in the same place if there has already been alternariosis.









































