Zanahoria
How to recognize and combat carrot chopping
Chopping The Carrot
Oomycete
Type:
Risk to the plant:
HIGH
Pythium Violae
Pathogen:
Phytophthora

WHO CAUSES IT?
Pythium violae is a pathogen belonging to the group of oomycetes, organisms that resemble fungi but are closer to algae in evolutionary terms. This pathogen is known for its ability to survive in soil and plant residues, persisting in adverse conditions through the production of resistant spores called oospores. Pythium violae is activated under conditions of high humidity and moderate temperatures, when it produces motile zoospores that swim in soil water and seek roots of susceptible plants. Once these zoospores find a suitable root, they attach to it and penetrate the tissues, initiating infection. This process results in the degradation of root cells, which facilitates the colonization of the pathogen and the dispersal of new spores to continue the infectious cycle.
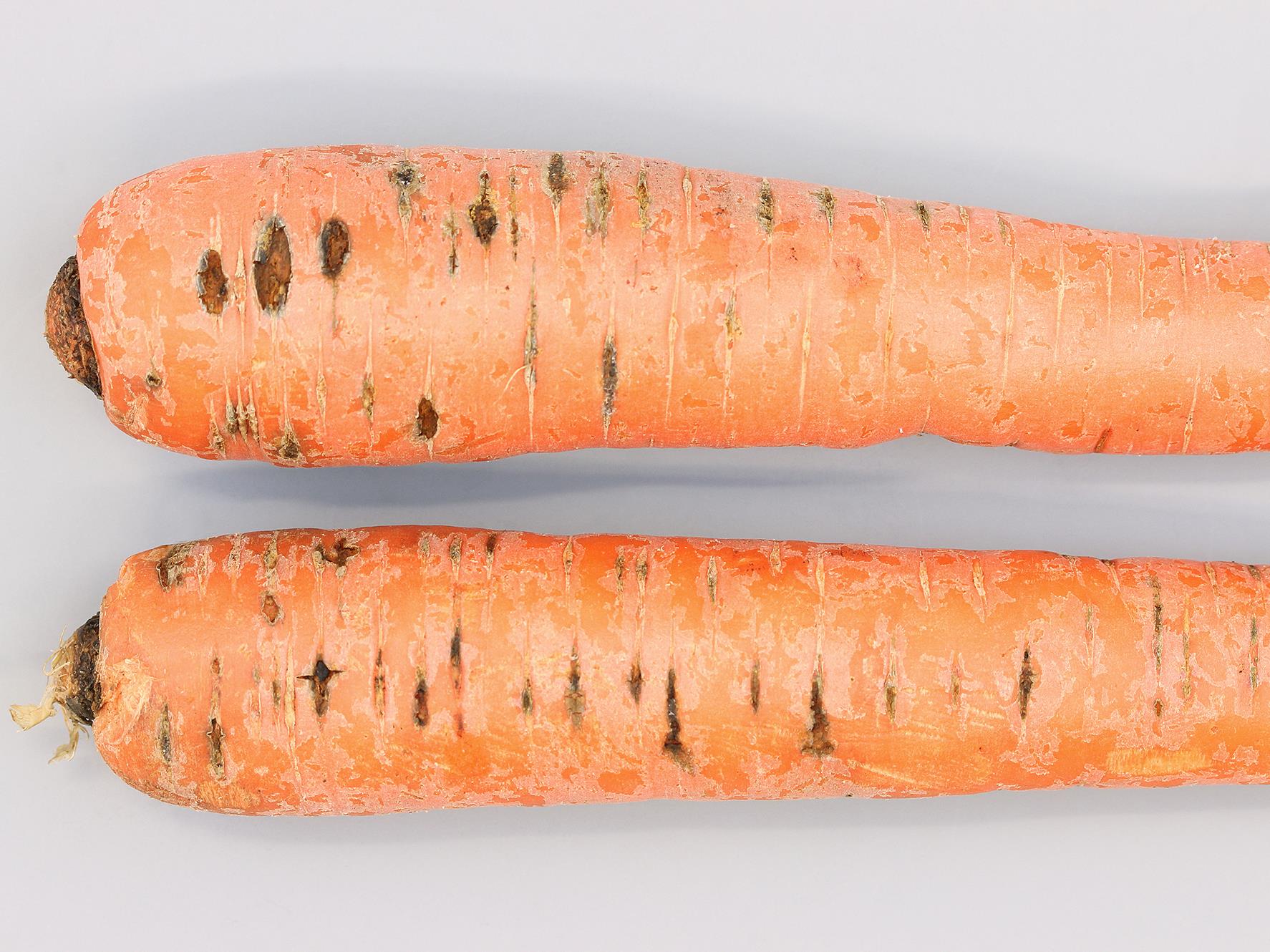
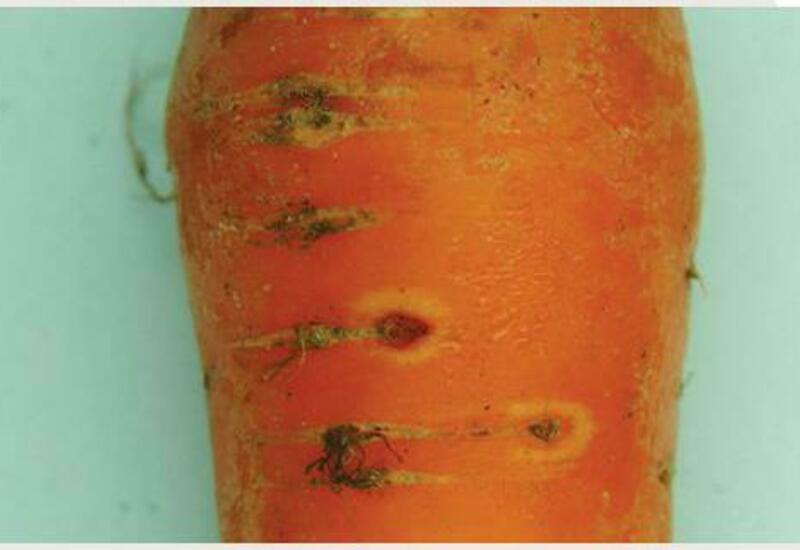
SYMPTOMS
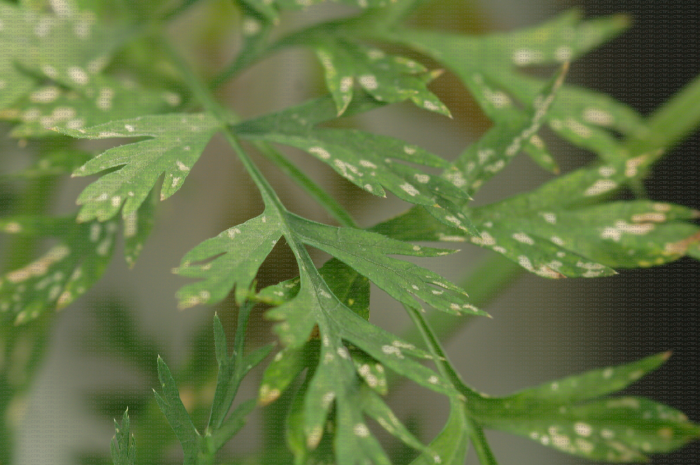
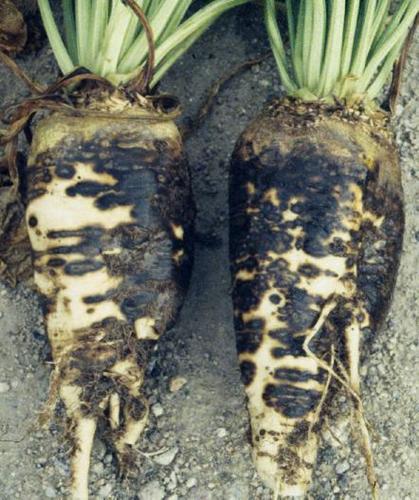
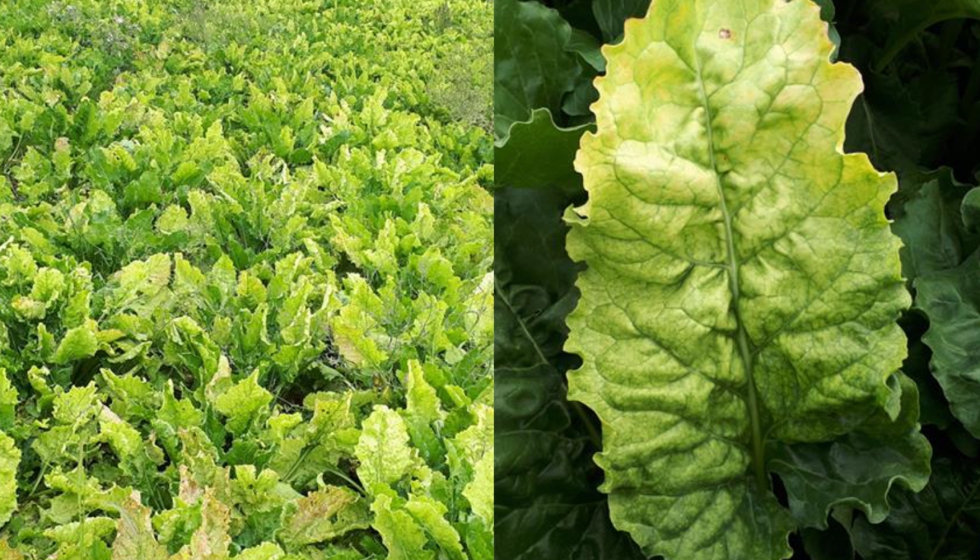
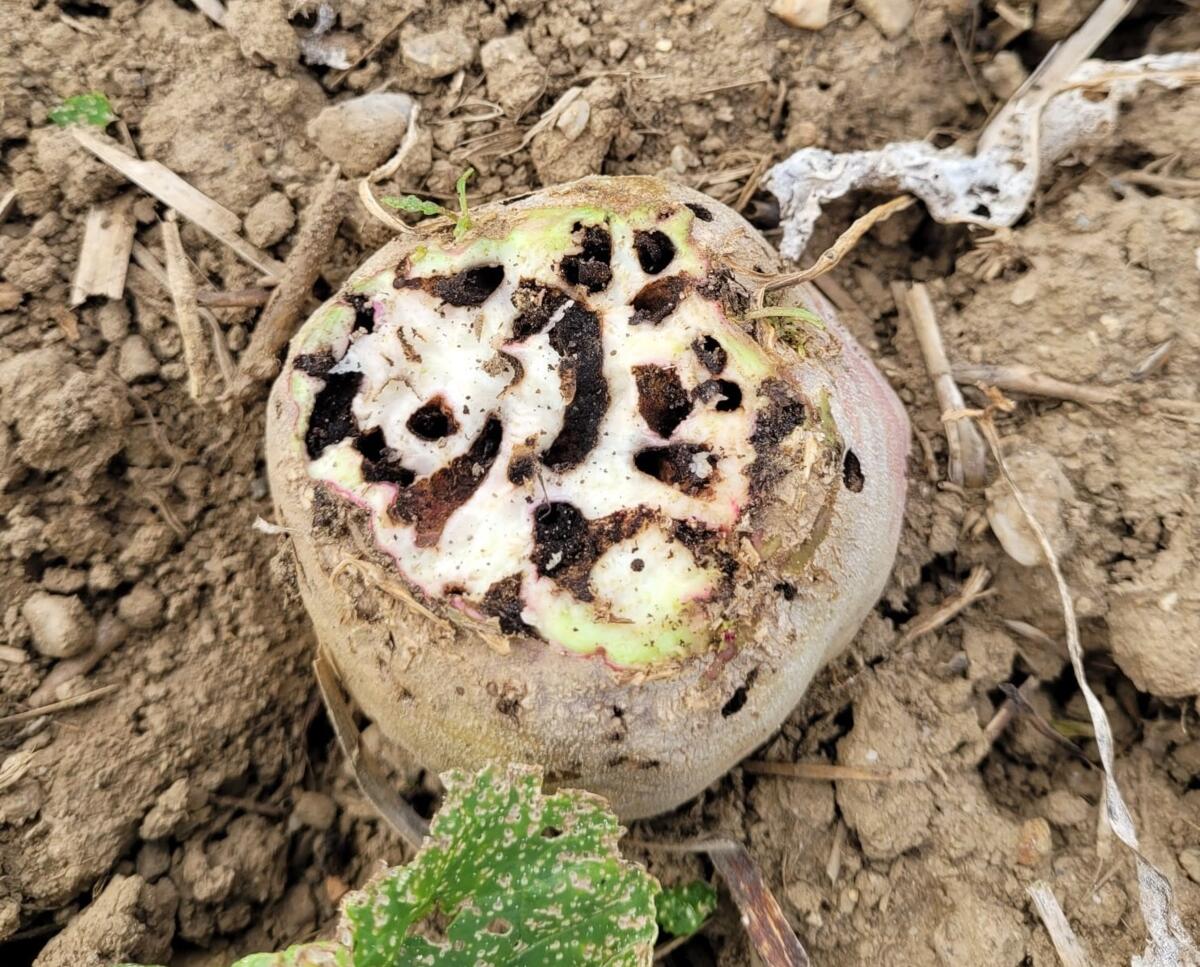
The disease known as carrot pitting, caused by Pythium violae, is a significant threat to this crop, causing losses in both quality and yield. Carrots affected by this disease present symptoms that manifest mainly in the roots, leading to a reduction in the commercial value of the crop. Pythium violae infection can cause root decay and, in severe cases, plant death.
- Dark, sunken Taches on the roots
- Root decomposition
- Malformations and deformations of carrots
- Reduction of plant growth
- Wilting in the upper leaves
- Premature death of affected plants

DEVELOPMENT CONDITIONS
Temperature:
15°C - 25°C
Humidity:
80% - 100%
HOW IS IT SPREAD?
Contaminated irrigation water, Infected plant residues, Cultivation tools and equipment, Movement of infested soil
HOW TO ELIMINATE IT?
Home treatments
Natural allies
There are no natural allies
Chemical treatments
RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS TO ELIMINATE THE PEST
REPELLENT PLANTS
-
RECOMMENDATIONS
- Avoid waterlogging pots or soil, make sure drainage is good.
- Water in the mornings so the soil dries during the day.
- Do not use soil or compost that has been in contact with diseased plants.
- Clean gardening tools after use.
- If a plant is very affected, remove it to prevent it from infecting the others.
- If necessary, use specific products with antifungal effect, always following the manufacturer's instructions.





























