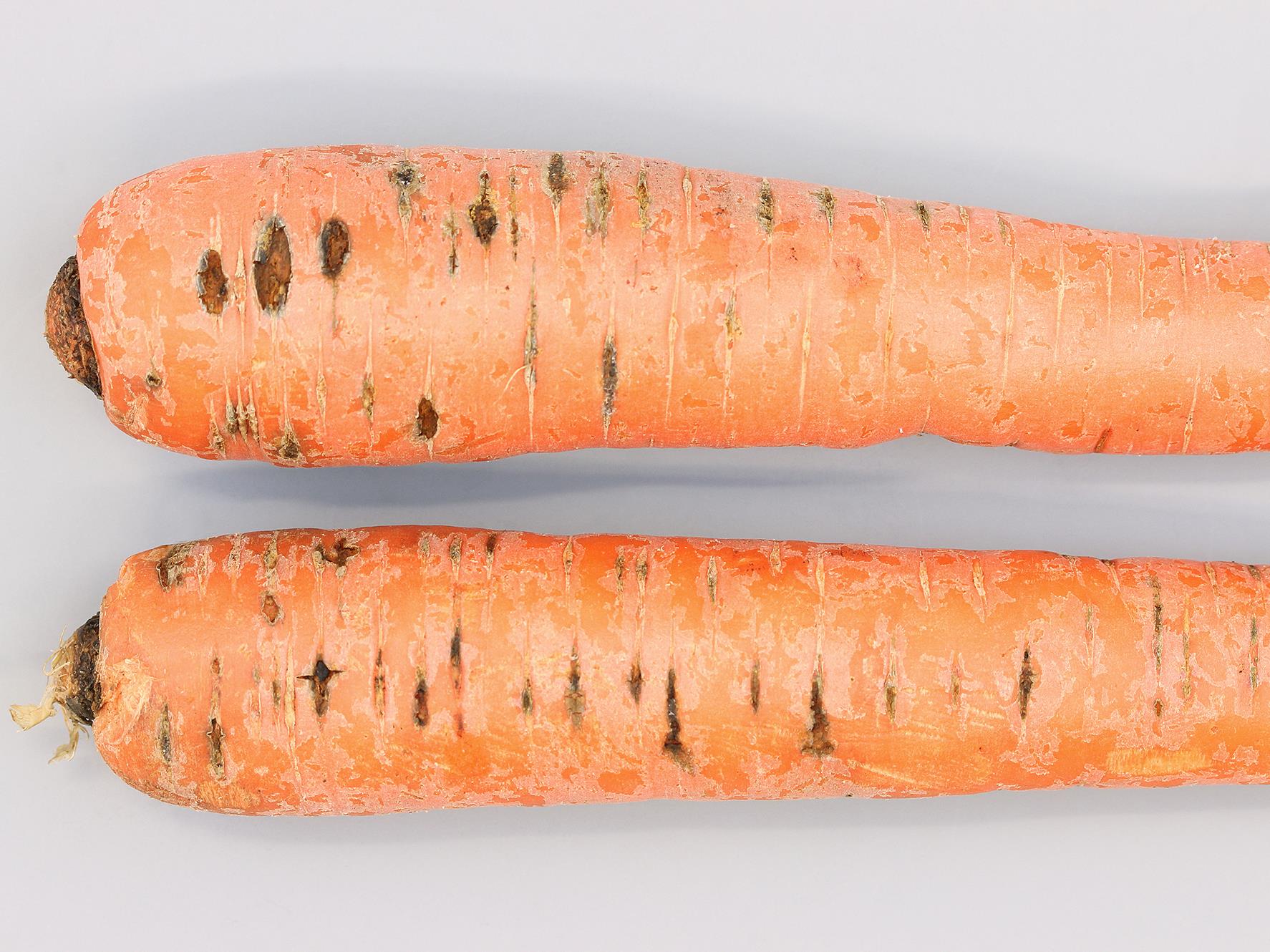
Zanahoria
How to recognize and combat carrot blight
Carrot Blight
Fungus
Type:
Risk to the plant:
HIGH
Septoria Carotae
Pathogen:
Septoriosis

WHO CAUSES IT?
Septoria carotae is a phytopathogenic fungus that causes a disease known as carrot blight. This fungus survives on infected plant remains and in the soil as resistant spores. During periods of high humidity and moderate temperatures, these spores germinate and release conidia, which are asexual spores that are dispersed by wind and rainwater. Conidia land on carrot foliage, where they germinate and penetrate tissues through stomata or wounds. Once inside the plant, the fungus colonizes the tissues, causing necrosis and producing new spores that spread to continue the infectious process in other plants. The infection spreads rapidly in moist conditions, especially when leaves are wet for long periods.
SYMPTOMS
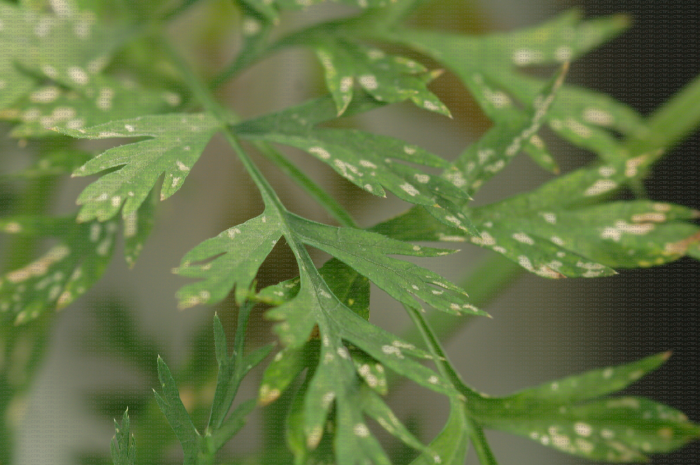
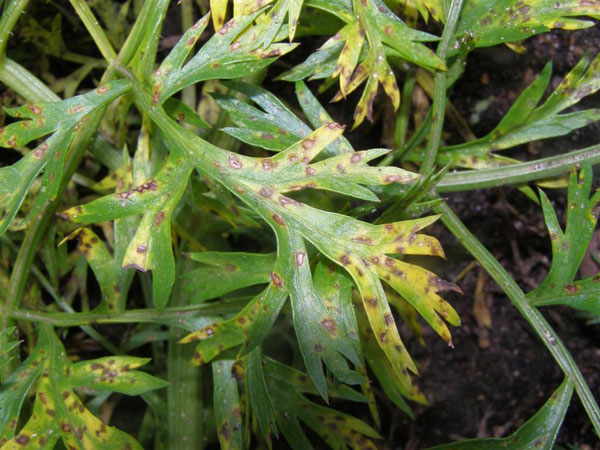
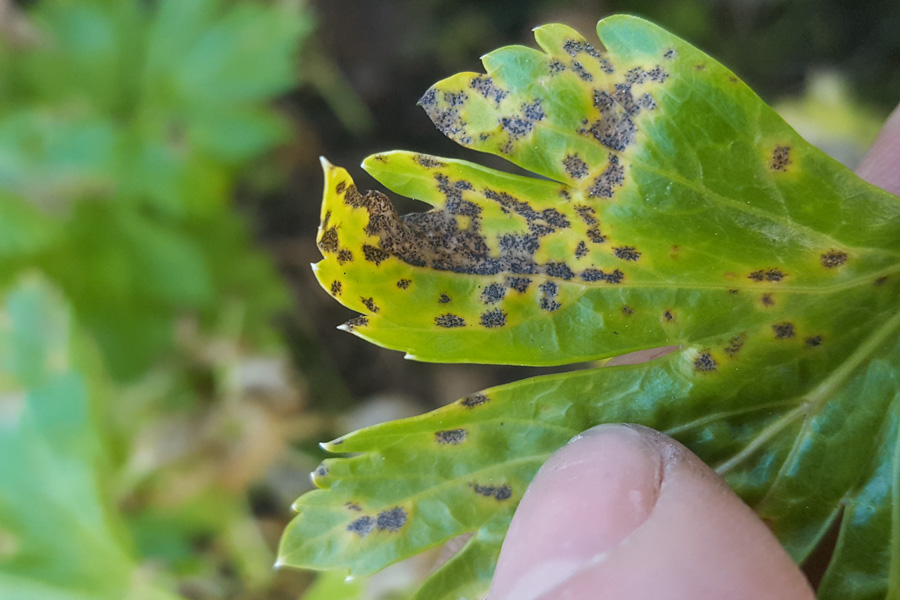
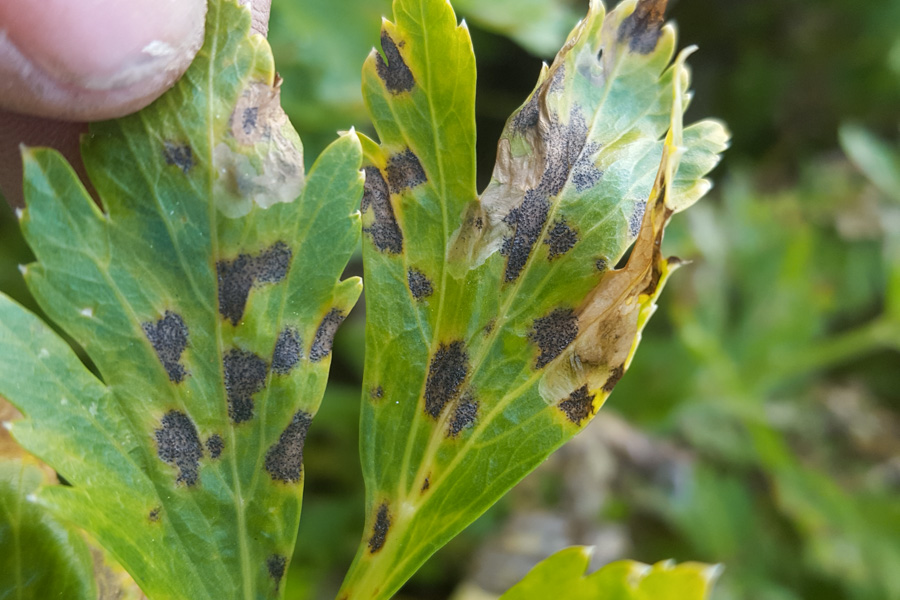
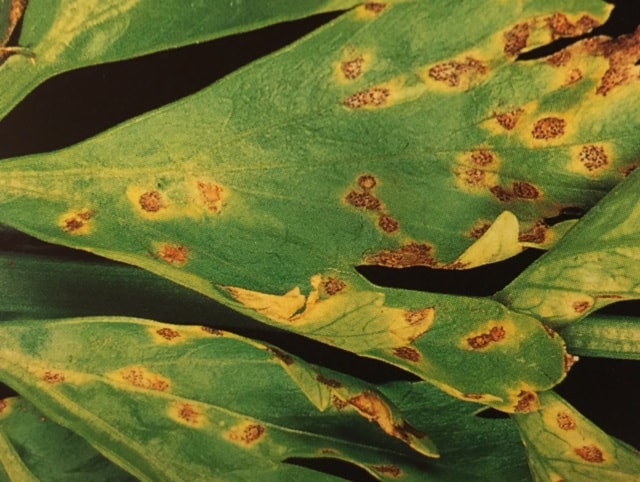
Carrot blight caused by Septoria carotae causes leaf Taches that can lead to defoliation and weakening of plants, seriously affecting crop quality and yield. Infected carrots show obvious signs on the foliage, which become more visible as the disease progresses.
- Small brown or black Taches on the leaves
- Taches surrounded by yellow halos
- Taches that enlarge and merge, causing necrosis
- Severe defoliation in advanced cases
- Reduction of plant growth
- General weakening of the plant

DEVELOPMENT CONDITIONS
Temperature:
15°C - 25°C
Humidity:
80% - 100%
HOW IS IT SPREAD?
Wind, Rainwater, Infected crop remains, Contaminated tools and equipment, Infected seeds
HOW TO ELIMINATE IT?
Home treatments
There are no home treatments
Natural allies
Chemical treatments
There are no treatments for this disease. Treatments are directed at the insect vectors that transmit it. See insect treatments.
RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS TO ELIMINATE THE PEST
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Effective against all types of fungi
PLANTAS REPELENTES
-
RECOMMENDATIONS
- Remove and eliminate infected leaves at the first sign of the disease.
- Avoid wetting the leaves when watering, water directly to the ground.
- Make sure the plants have good ventilation and are not too close together.
- Disinfect gardening tools after using them.
- Do not leave remains of diseased plants on the ground.
- Rotate crops if possible, to prevent the fungus from reappearing.
- You can apply a preventive fungicide if the disease is recurrent.









































