
Red Spider
Tetranychus Urticae
Pathogen:
Insect
Type:
Risk:
HIGH
Araña roja
Plantas decorativas de jardín y/o interior


WHO CAUSES IT?
Tetranychus urticae, commonly known as spider mite, is a tiny mite that infests various plants. Adult females deposit their spherical, transparent eggs on the lower surface of the leaves. These eggs hatch within a few days, giving rise to six-legged larvae that quickly transform into eight-legged nymphs. Nymphs go through two instars before becoming adults. This development can be completed in less than a week under favorable conditions, allowing spider mite populations to multiply rapidly. Adult females, reddish or greenish-yellow in color with two dark dorsal Taches, can live for several weeks, during which they lay hundreds of eggs, thus ensuring the continuity of the infestation.
SYMPTOMS
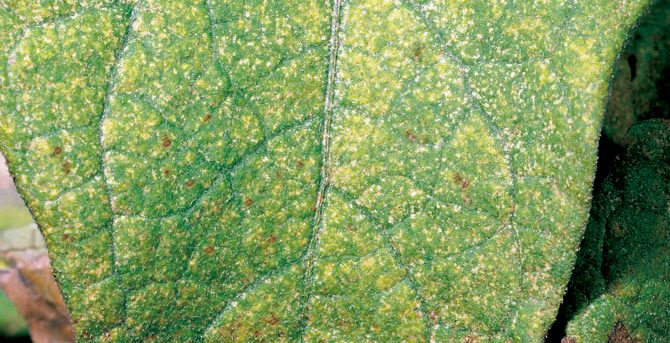
Infestation by Tetranychus urticae in plants causes the disease known as red spider, which weakens and severely damages plants. These mites feed by sucking the cellular contents of the leaves, which reduces the photosynthetic capacity and causes considerable stress in the plants. Symptoms of this disease include:
- Appearance of yellow or tan Taches on the leaves.
- Discolored and dry leaves.
- Mottled or spotted leaf tissues.
- Premature loss of leaves.
- Reduction of plant vigor and growth.
- Presence of fine cobwebs on the underside of the leaves and between the shoots.
- Visible damage to shoots and fruits, especially in cases of severe infestations.
TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY
20°C - 30°C
40% - 60%
TRANSMISSION PATHS
Wind, contaminated garden tools, direct contact between plants, exchange of infected plants, flying insects
Do you want to remove this pest? Choose how you want to treat it.
TREATMENTS
Chemical treatment
• ABAMECTIN 1.8% [EC] P/V
• RAPE OIL 1.53% [AL] P/V
• RAPE OIL 848.24 g/l [EC] P/V
• ORANGE OIL 60g/L [ME] P/S
• PARAFFIN OIL (CAS [97862-82-3]) 80% [EC] P/V
• SULFUR 80% [SC] P/V
• SULFUR 80% [WG] P/P
• SULFUR 80% [WP] P/P
• BIPHENAZATE 24% [SC] P/V
• PHENPIROXIMATE 5.12% [SC] P/V
• HEXITIAZOX 10% [WP] P/P
• MILBEMECTIN 0.93% [EC] P/V
• POTASSIUM SALTS OF UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS C7-C18 & C18 (CAS [67701-09-1] 515g/L [SL] P/V
• POTASSIUM SALTS OF UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS C7-C18 & C18 10.2g/L [AL] P/V
• TAU-FLUVALINATE 24% [EW] P/V
Authorized treatments in organic farming
• RAPE OIL 1.53% [AL] P/V
• RAPE OIL 848.24 g/l [EC] P/V
• ORANGE OIL 60g/L [ME] P/S
• PARAFFIN OIL (CAS [97862-82-3]) 80% [EC] P/V
• SULFUR 80% [SC] P/V
• SULFUR 80% [WG] P/P
• SULFUR 80% [WP] P/P
• POTASSIUM SALTS OF UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS C7-C18 & C18 (CAS [67701-09-1] 515g/L [SL] P/V
• POTASSIUM SALTS OF UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS C7-C18 & C18 10.2g/L [AL] P/V
Biological control
• AMBLYSEIUS ANDERSONI (parasitoid and predatory mites)
• BEAUVERIA BASSIANA (STRAIN ATCC 74040) 2.3% (2.3X10E7 VIABLE SPORES/ML) [OD] P/V
• NEOSEIULUS CALIFORNICUS (parasitoid and predatory mites)
• PHYTOSEIULUS PERSIMILIS (parasitoid and predatory mites)
Recommendations
- Regularly monitor plants for the presence of mites.
- Use horticultural oils and insecticidal soaps to suffocate and eliminate mites.
- Introduce and encourage the presence of natural enemies such as predatory mites (Phytoseiulus persimilis).
- Maintain adequate ventilation and humidity in the crop to discourage the development of red spiders.
- Apply balanced irrigation and fertilization to keep plants vigorous and less susceptible to infestations.
- Use sticky traps to monitor the presence of flying mites.
- Carry out crop rotations to interrupt the life cycle of the red spider.
- Implement preventive phytosanitary treatments during times of greatest risk.
- Prune and remove infested parts of the plant to reduce the mite population.
- Avoid excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers, which can promote the growth of red spider mites.
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Effective against all types of fungi
TREATMENTS
Homemade treatments
There are no home treatments
Natural allies
Chemical treatments
There are no treatments for this disease. Treatments are directed at the insect vectors that transmit it. See insect treatments.
RECOMMENDATIONS
- Check the back of the leaves frequently, especially in dry weather.
- Spray water on the leaves to increase humidity and prevent them from settling.
- Keep plants healthy with good watering and adequate light.
- If you see cobwebs or damage, clean the leaves with a damp cloth or pressurized water.
- Use potassium soap or neem oil every few days until they disappear.
REPELLENT PLANTS
Rosemary, Dill, Coriander
RECOMMENDED PRODUCTS TO ELIMINATE THIS PEST
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Effective against all types of fungi
*The recommended treatments are still recommendations according to the databases of the authorities and at no time do they replace the guidelines established according to the legislation of each country
*The products shown are recommendations and are not our own products. As Amazon Associates, we earn revenue from purchases of recommended products.






















