
Carrot Scab
Streptomyces Scabies
Pathogen:
Type:
Bacterium
Risk:
INTERMEDIATE

Zanahoria
Bacteriosis
WHO CAUSES IT?
Streptomyces scabies is a gram-positive bacteria belonging to the genus Streptomyces, known to cause scab in various plants, especially tubers such as carrots. This bacteria is commonly found in soil and produces spores that can survive in adverse conditions for long periods. Streptomyces scabies spreads mainly through soil and infected plant residues. Once the spores come into contact with carrot roots, they germinate and colonize the plant tissues, producing toxins that cause lesions and scabs to form. These bacteria can persist in the soil for several years, which complicates their management and control.
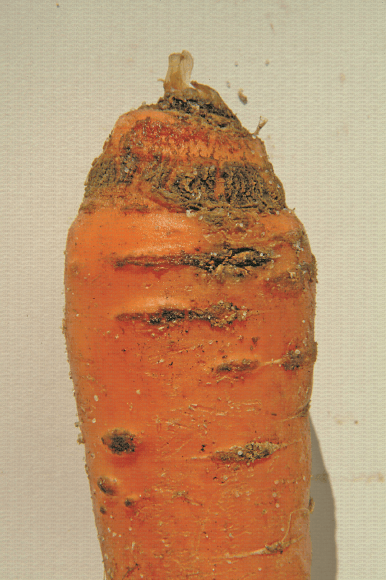
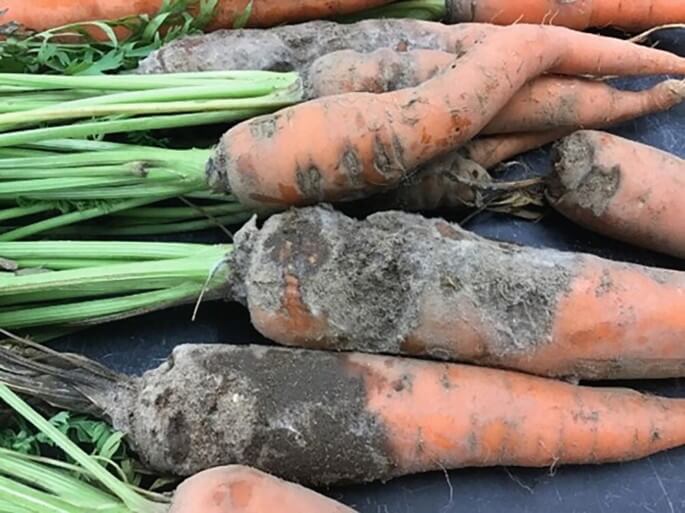
SYMPTOMS
Carrot scab, caused by Streptomyces scabies, is a disease that primarily affects the appearance and quality of carrot roots. Infected roots develop superficial lesions that can become rough and warty, decreasing the commercial value of the crop.
- Rough lesions and scabs on the surface of the carrots.
- Brown discoloration in affected areas.
- Deformations and cracks in the roots.
- Warty and rough appearance.
- Reduction in plant growth and vigor.
- Loss of commercial quality of carrots.

TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY
18°C - 26°C
60% - 85%
TRANSMISSION ROUTES
Infected soil, crop residues, contaminated irrigation water, agricultural tools, wind, infected seeds
Do you want to remove this disease? Choose how you want to treat it.
TREATMENTS
Chemical treatments
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 35% (EXPR. IN CU) [WG] P/P
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 37.5% (EXPR. IN CU) [WG] P/P
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 38% (EXPR. IN CU) [SC] P/V
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 50% (EXPR. IN CU) [WP] P/P
• CUPROCALCIC SULFATE 12.4% (EXPR. IN CU) [SC] P/V
• CUPROCALCIC SULFATE 20% (EXPR. IN CU) [WG] P/P
Authorized treatments in organic farming
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 35% (EXPR. IN CU) [WG] P/P
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 37.5% (EXPR. IN CU) [WG] P/P
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 38% (EXPR. IN CU) [SC] P/V
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 50% (EXPR. IN CU) [WP] P/P
• CUPROCALCIC SULFATE 12.4% (EXPR. IN CU) [SC] P/V
• CUPROCALCIC SULFATE 20% (EXPR. IN CU) [WG] P/P
Biological control
• BACILLUS AMYLOLIQUEFACIENS (subsp. plantarum, strain D747) 25% [WG] P/P
• BACILLUS SUBTILIS (STRAIN QST 713) 1.34% [SC] P/V
Recommendations
- Carry out crop rotation, avoiding planting carrots and other susceptible hosts in the same place for several years.
- Use carrot varieties resistant to Streptomyces scabies.
- Implement soil management practices that favor the growth of beneficial microorganisms, such as the application of compost and organic matter.
- Maintain the soil pH at slightly acidic levels, since Streptomyces scabies prefers alkaline soils.
- Avoid excess moisture in the soil, since poorly drained soils can favor the proliferation of bacteria.
- Apply treatments with specific biological and bactericidal agents following technical recommendations.
- Regularly monitor crops and eliminate infected plants to reduce the source of inoculum in the field.
- Clean and disinfect agricultural tools to prevent the spread of bacteria.
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Effective against all types of fungi
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
*The recommended treatments are recommendations based on the authorities' databases and do not replace in any way the guidelines established by the legislation of each country.
*Products shown are recommendations and not our own products. As Amazon Associates, we earn revenue from purchases of recommended products.
TREATMENTS
Homemade remedies
There are no home treatments
Natural allies
Chemical treatments
There are no treatments for this disease. Treatments are directed at the insect vectors that transmit it. See insect treatments.
RECOMMENDATIONS
REPELLENT PLANTS
EFFECTIVE PRODUCTS TO ELIMINATE THIS DISEASE
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Effective against all types of fungi
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
*The recommended treatments are recommendations based on the authorities' databases and do not replace in any way the guidelines established by the legislation of each country.
*Products shown are recommendations and not our own products. As Amazon Associates, we earn revenue from purchases of recommended products.






















