
Bacteriosis
Bacterial Pustule
Xanthomonas Campestris Pv. Glycines
Pathogen:
Bacterium
Type:
Risk to the plant:
INTERMEDIATE

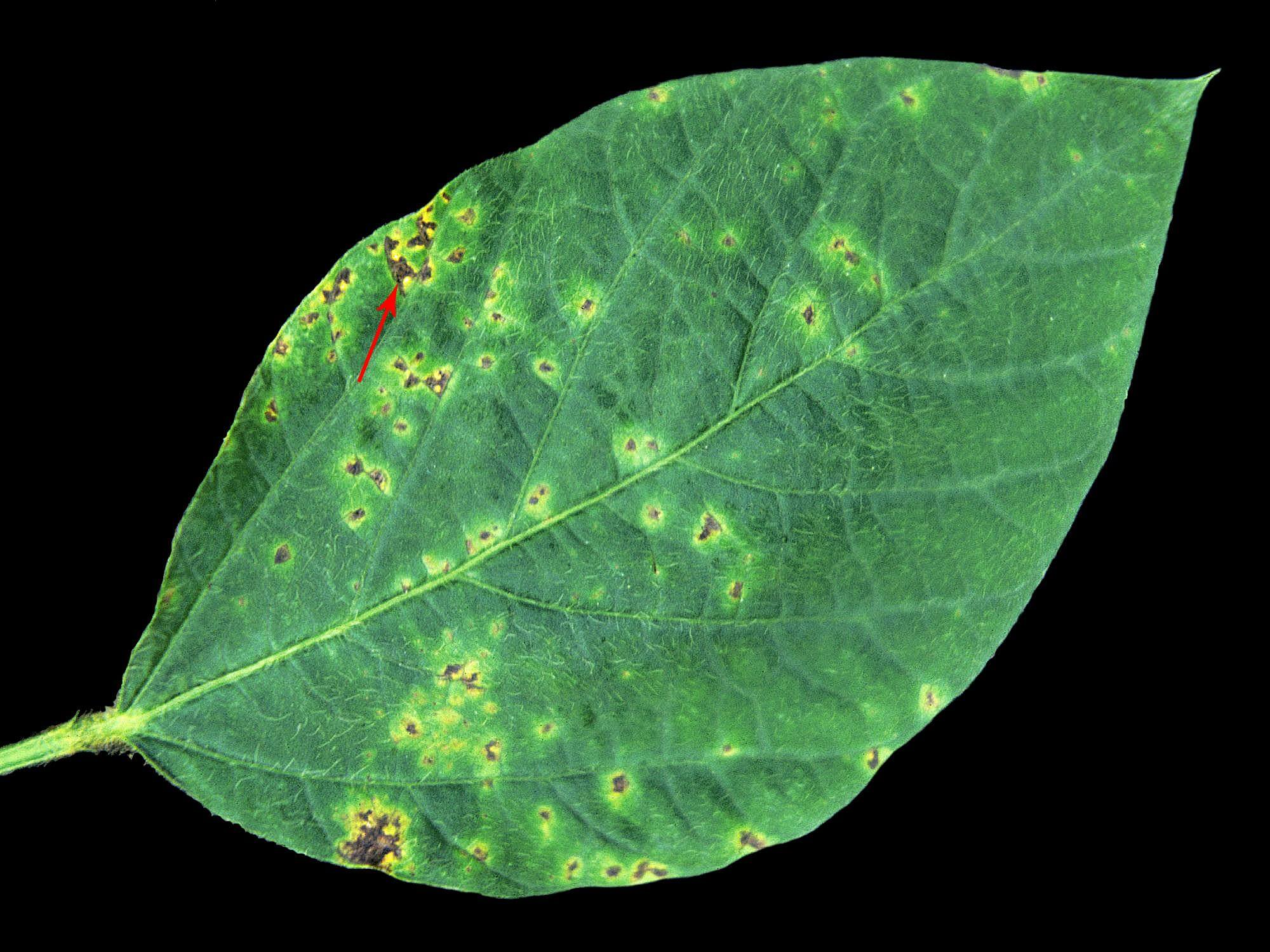

DESCRIPTION
WHO CAUSES IT?
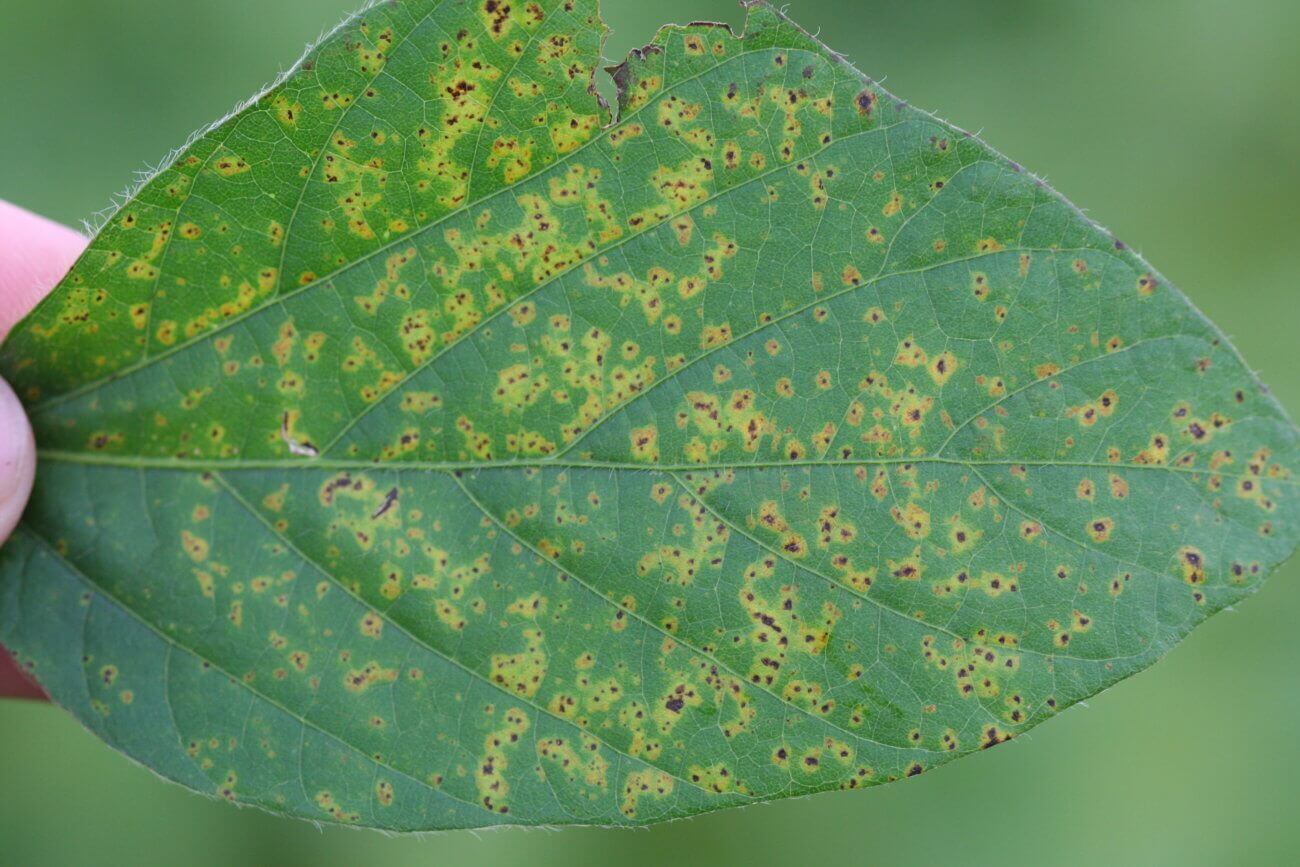
Bacterial pustule, caused by the bacteria Xanthomonas campestris pv. glycines, is an important disease that affects soybean crops in many regions of the world. This bacteria is capable of causing significant damage to soybean plants, which can result in economic losses for farmers.
SYMPTOMS
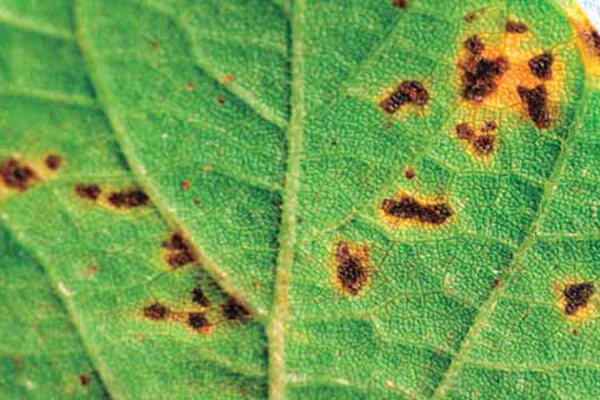
In soybeans, bacterial pustule produces symptoms that include the appearance of necrotic lesions on the leaves, stems and pods of the plant. These lesions usually have a sunken appearance and may be surrounded by a yellowish halo. Over time, the lesions can expand and cause premature defoliation, which can reduce crop yield.


TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY
25°C - 30°C
70% - 90%

HOW IS IT SPREAD?
Infected seeds, plant remains, irrigation water, agricultural tools, insects.

HOW TO REMOVE IT?
Home remedies
There are no home treatments
Chemical treatments
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 35% (exp. in Cu) [WG] P/P
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 38% (EXPR. IN CU) [SC] P/V
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 50% (EXPR. IN CU) [WP] P/P
Authorized treatments in organic farming
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 35% (exp. in Cu) [WG] P/P
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 38% (EXPR. IN CU) [SC] P/V
• COPPER OXYCHLORIDE 50% (EXPR. IN CU) [WP] P/P
Insect allies
PREDATORY MITES
LADYBUGS
LACEWINGS
PARASITIC WASPS
HOVERFLIES OR PARASITIC FLIES
PREDATORY BUGS
There are no natural allies
Mycodiplosis oidii (predatory mosquito)
EFFECTIVE PRODUCTS TO ELIMINATE THIS DISEASE
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Effective against all types of fungi
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
Sponsored link
To prevent and control bacterial pustule in soybean crops, it is important to implement integrated pest management practices. This includes the use of pathogen-free seeds, crop rotation, weed control and the application of specific bactericides at critical moments in the crop cycle.
























